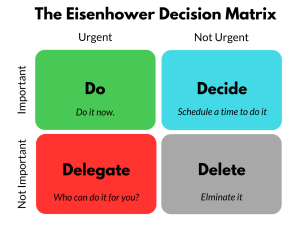
Project Management (PM) is the discipline of planning, organizing, and executing work to achieve specific goals within defined constraints (time, budget, scope). It ensures teams deliver results efficiently—whether building software, launching a product, or constructing a bridge.
Key Components of Project Management
-
Scope
-
Clearly defines what the project will deliver (e.g., a new app feature, a marketing campaign).
-
Avoids “scope creep” (uncontrolled changes).
-
-
Time
-
Sets deadlines and milestones (e.g., Gantt charts, Agile sprints).
-
-
Cost
-
Manages budgets and resources (people, tools, materials).
-
-
Quality
-
Ensures deliverables meet standards (e.g., user testing, compliance checks).
-
-
Stakeholders
-
Aligns teams, clients, and executives on expectations.
-
Popular Project Management Methodologies
| Method | Focus | Example Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Waterfall | Linear, sequential phases | Construction, manufacturing |
| Agile | Iterative, flexible | Software development |
| Scrum | Short sprints (2-4 weeks) | Tech startups, product teams |
| Kanban | Visual workflow (tasks as cards) | Support teams, content creation |
| Lean | Minimize waste | Manufacturing, healthcare |
Why Project Management Matters
✅ Efficiency – Reduces wasted time/resources.
✅ Risk Control – Identifies problems early.
✅ Accountability – Clarifies roles (who does what).
✅ Goal Alignment – Keeps teams focused on outcomes.
Example: A project manager at a tech company might:
-
Break down an app launch into tasks (design, coding, testing).
-
Assign deadlines using Jira or Trello.
-
Hold daily stand-up meetings (Agile/Scrum).
Tools Project Managers Use
-
Planning: Microsoft Project, Asana
-
Collaboration: Slack, Notion
-
Tracking: Trello (Kanban), Jira (Scrum)
Project Management in Tech & Beyond
-
Software Dev: Managing sprints for a new feature.
-
Construction: Coordinating contractors for a skyscraper.
-
Events: Planning a conference timeline.
Fun Fact: The Pyramids of Giza were likely built using early PM techniques!